Ta strona została przetłumaczona przez PageTurner AI (beta). Nie jest oficjalnie zatwierdzona przez projekt. Znalazłeś błąd? Zgłoś problem →
Emituj zdarzenia w modułach natywnych
W niektórych sytuacjach możesz potrzebować modułu natywnego, który nasłuchuje zdarzeń w warstwie platformy i emituje je do warstwy JavaScript, aby Twoja aplikacja mogła reagować na takie natywne zdarzenia. W innych przypadkach możesz mieć długotrwałe operacje, które emitują zdarzenia, aby interfejs użytkownika mógł być aktualizowany w miarę ich występowania.
Oba przypadki są dobrymi przykładami użycia emisji zdarzeń z modułów natywnych. W tym przewodniku nauczysz się, jak to zrobić.
Emitowanie zdarzenia po dodaniu nowego klucza do pamięci
W tym przykładzie nauczysz się emitować zdarzenie, gdy do pamięci zostanie dodany nowy klucz. Zmiana wartości istniejącego klucza nie spowoduje emisji zdarzenia – emisja nastąpi tylko przy dodaniu nowego klucza.
Ten przewodnik kontynuuje tematykę z przewodnika po modułach natywnych.
Upewnij się, że znasz tamten przewodnik, zanim zagłębisz się w ten, najlepiej implementując wcześniejszy przykład.
Krok 1: Aktualizacja specyfikacji NativeLocalStorage
Pierwszym krokiem będzie zaktualizowanie specyfikacji modułu NativeLocalStorage, aby poinformować React Native, że moduł może emitować zdarzenia.
- TypeScript
- Flow
Open the NativeLocalStorage.ts file and update it as it follows:
+import type {TurboModule, CodegenTypes} from 'react-native';
import {TurboModuleRegistry} from 'react-native';
+export type KeyValuePair = {
+ key: string,
+ value: string,
+}
export interface Spec extends TurboModule {
setItem(value: string, key: string): void;
getItem(key: string): string | null;
removeItem(key: string): void;
clear(): void;
+ readonly onKeyAdded: CodegenTypes.EventEmitter<KeyValuePair>;
}
export default TurboModuleRegistry.getEnforcing<Spec>(
'NativeLocalStorage',
);
Open the NativeLocalStorage.js file and update it as it follows:
// @flow
+import type {TurboModule, CodegenTypes} from 'react-native';
import {TurboModule, TurboModuleRegistry} from 'react-native';
+export type KeyValuePair = {
+ key: string,
+ value: string,
+}
export interface Spec extends TurboModule {
setItem(value: string, key: string): void;
getItem(key: string): ?string;
removeItem(key: string): void;
clear(): void;
+ onKeyAdded: CodegenTypes.EventEmitter<KeyValuePair>
}
export default (TurboModuleRegistry.get<Spec>(
'NativeLocalStorage'
): ?Spec);
Korzystając z instrukcji import type, importujesz CodegenTypes z react-native, co obejmuje typ EventEmitter. Pozwala to zdefiniować właściwość onKeyAdded za pomocą CodegenTypes.EventEmitter<KeyValuePair>, określając, że zdarzenie będzie emitować ładunek typu KeyValuePair.
Gdy zdarzenie jest emitowane, oczekujesz, że otrzyma parametr typu KeyValuePair.
Krok 2: Generowanie kodu za pomocą Codegen
Po zaktualizowaniu specyfikacji modułu natywnego musisz ponownie uruchomić Codegen, aby wygenerować artefakty w kodzie natywnym.
Jest to ten sam proces przedstawiony w przewodniku dotyczącym modułów natywnych.
- Android
- iOS
Codegen is executed through the generateCodegenArtifactsFromSchema Gradle task:
cd android
./gradlew generateCodegenArtifactsFromSchema
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 837ms
14 actionable tasks: 3 executed, 11 up-to-date
This is automatically run when you build your Android application.
Codegen is run as part of the script phases that's automatically added to the project generated by CocoaPods.
cd ios
bundle install
bundle exec pod install
The output will look like this:
...
Framework build type is static library
[Codegen] Adding script_phases to ReactCodegen.
[Codegen] Generating ./build/generated/ios/ReactCodegen.podspec.json
[Codegen] Analyzing /Users/me/src/TurboModuleExample/package.json
[Codegen] Searching for Codegen-enabled libraries in the app.
[Codegen] Found TurboModuleExample
[Codegen] Searching for Codegen-enabled libraries in the project dependencies.
[Codegen] Found react-native
...
Krok 3: Aktualizacja kodu aplikacji
Czas zaktualizować kod aplikacji, aby obsłużyć nowe zdarzenie.
Otwórz plik App.tsx i zmodyfikuj go w następujący sposób:
import React from 'react';
import {
+ Alert,
+ EventSubscription,
SafeAreaView,
StyleSheet,
Text,
TextInput,
Button,
} from 'react-native';
import NativeLocalStorage from './specs/NativeLocalStorage';
const EMPTY = '<empty>';
function App(): React.JSX.Element {
const [value, setValue] = React.useState<string | null>(null);
+ const [key, setKey] = React.useState<string | null>(null);
+ const listenerSubscription = React.useRef<null | EventSubscription>(null);
+ React.useEffect(() => {
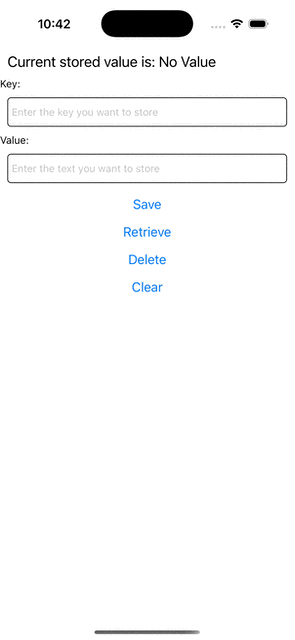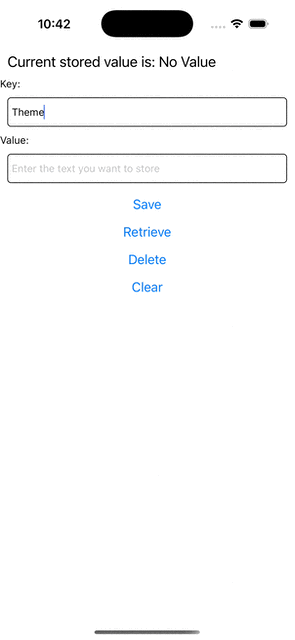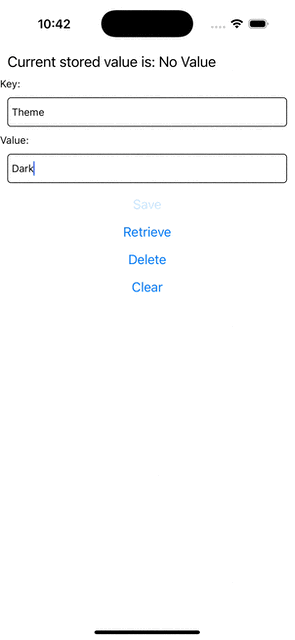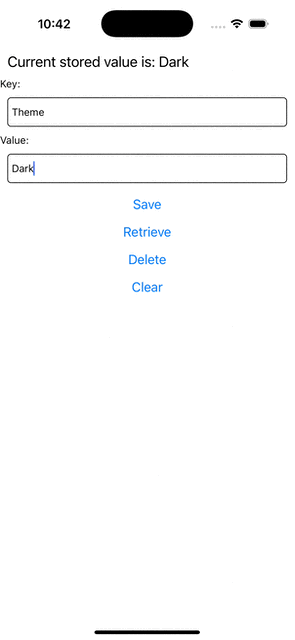
+ listenerSubscription.current = NativeLocalStorage?.onKeyAdded((pair) => Alert.alert(`New key added: ${pair.key} with value: ${pair.value}`));
+ return () => {
+ listenerSubscription.current?.remove();
+ listenerSubscription.current = null;
+ }
+ }, [])
const [editingValue, setEditingValue] = React.useState<
string | null
>(null);
- React.useEffect(() => {
- const storedValue = NativeLocalStorage?.getItem('myKey');
- setValue(storedValue ?? '');
- }, []);
function saveValue() {
+ if (key == null) {
+ Alert.alert('Please enter a key');
+ return;
+ }
NativeLocalStorage?.setItem(editingValue ?? EMPTY, key);
setValue(editingValue);
}
function clearAll() {
NativeLocalStorage?.clear();
setValue('');
}
function deleteValue() {
+ if (key == null) {
+ Alert.alert('Please enter a key');
+ return;
+ }
NativeLocalStorage?.removeItem(key);
setValue('');
}
+ function retrieveValue() {
+ if (key == null) {
+ Alert.alert('Please enter a key');
+ return;
+ }
+ const val = NativeLocalStorage?.getItem(key);
+ setValue(val);
+ }
return (
<SafeAreaView style={{flex: 1}}>
<Text style={styles.text}>
Current stored value is: {value ?? 'No Value'}
</Text>
+ <Text>Key:</Text>
+ <TextInput
+ placeholder="Enter the key you want to store"
+ style={styles.textInput}
+ onChangeText={setKey}
+ />
+ <Text>Value:</Text>
<TextInput
placeholder="Enter the text you want to store"
style={styles.textInput}
onChangeText={setEditingValue}
/>
<Button title="Save" onPress={saveValue} />
+ <Button title="Retrieve" onPress={retrieveValue} />
<Button title="Delete" onPress={deleteValue} />
<Button title="Clear" onPress={clearAll} />
</SafeAreaView>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
text: {
margin: 10,
fontSize: 20,
},
textInput: {
margin: 10,
height: 40,
borderColor: 'black',
borderWidth: 1,
paddingLeft: 5,
paddingRight: 5,
borderRadius: 5,
},
});
export default App;
Oto kilka istotnych zmian, na które należy zwrócić uwagę:
-
Musisz zaimportować typ
EventSubscriptionzreact-native, aby obsłużyćEventSubscription -
Musisz użyć
useRef, aby śledzić referencję doEventSubscription -
Rejestrujesz nasłuchiwacz za pomocą hooka
useEffect. FunkcjaonKeyAddedprzyjmuje funkcję zwrotną z obiektem typuKeyValuePairjako parametr. -
Funkcja zwrotna dodana do
onKeyAddedjest wykonywana za każdym razem, gdy zdarzenie jest emitowane z warstwy natywnej do JavaScript. -
W funkcji czyszczącej
useEffectusuwasz subskrypcję zdarzenia za pomocąremovei ustawiasz referencję nanull.
Pozostałe zmiany to standardowe modyfikacje w React służące ulepszeniu aplikacji pod kątem nowej funkcjonalności.
Krok 4: Napisz swój kod natywny
Przygotowawszy wszystko, zacznijmy pisać natywny kod platformy.
- Android
- iOS
Assuming you followed the guide for Android described in the Native Modules guide, what's left to do is to plug the code that emit the events in your app.
To do so, you have to:
- Open the
NativeLocalStorage.ktfile - Modify it as it follows:
package com.nativelocalstorage
import android.content.Context
import android.content.SharedPreferences
import com.nativelocalstorage.NativeLocalStorageSpec
+import com.facebook.react.bridge.Arguments
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext
+import com.facebook.react.bridge.WritableMap
class NativeLocalStorageModule(reactContext: ReactApplicationContext) : NativeLocalStorageSpec(reactContext) {
override fun getName() = NAME
override fun setItem(value: String, key: String) {
+ var shouldEmit = false
+ if (getItem(key) != null) {
+ shouldEmit = true
+ }
val sharedPref = getReactApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences("my_prefs", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
val editor = sharedPref.edit()
editor.putString(key, value)
editor.apply()
+ if (shouldEmit == true) {
+ val eventData = Arguments.createMap().apply {
+ putString("key", key)
+ putString("value", value)
+ }
+ emitOnKeyAdded(eventData)
+ }
}
override fun getItem(key: String): String? {
val sharedPref = getReactApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences("my_prefs", Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
val username = sharedPref.getString(key, null)
return username.toString()
}
First, you need to import a couple of types that you need to use to create the eventData that needs to be sent from Native to JS. These imports are:
import com.facebook.react.bridge.Argumentsimport com.facebook.react.bridge.WritableMap
Secondly, you need to implement the logic that actually emits the event to JS. In case of complex types, like the KeyValuePair defined in the specs, Codegen will generate a function that expects a ReadableMap as a parameter. You can create the ReadableMap by using the Arguments.createMap() factory method, and use the apply function to populate the map. It's your responsibility to make sure that the the keys you are using in the map are the same properties that are defined in the spec type in JS.
Assuming you followed the guide for iOS described in the Native Modules guide, what's left to do is to plug the code that emit the events in your app.
To do so, you have to:
- Open the
RCTNativeLocalStorage.hfile. - Change the base class from
NSObjecttoNativeLocalStorageSpecBase
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <NativeLocalStorageSpec/NativeLocalStorageSpec.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
-@interface RCTNativeLocalStorage : NSObject <NativeLocalStorageSpec>
+@interface RCTNativeLocalStorage : NativeLocalStorageSpecBase <NativeLocalStorageSpec>
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
- Open the
RCTNativeLocalStorage.mmfile. - Modify it to emit the events when needed, for example:
- (void)setItem:(NSString *)value key:(NSString *)key {
+ BOOL shouldEmitEvent = NO;
+ if (![self getItem:key]) {
+ shouldEmitEvent = YES;
+ }
[self.localStorage setObject:value forKey:key];
+ if (shouldEmitEvent) {
+ [self emitOnKeyAdded:@{@"key": key, @"value": value}];
+ }
}
The NativeLocalStorageSpecBase is a base class that provides the emitOnKeyAdded method and its basic implementation and boilerplate. Thanks to this class, you don't have to handle all the conversion between Objective-C and JSI that is required to send the event to JS.
In case of complex types, like the KeyValuePair defined in the specs, Codegen will generate a generic dictionary that you can populate on the native side. It's your responsibility to make sure that the the keys you are using in the dictionary are the same properties that are defined in the spec type in JS.
Krok 5: Uruchom swoją aplikację
Jeśli teraz spróbujesz uruchomić aplikację, powinieneś zaobserwować takie zachowanie.
 |  |